All too often investigating an IT incident translates to addressing only the symptoms, not the underlying causes.
Nexthink research has found that automating solutions for common incidents only reduces overall incidents by about 10%. To achieve more significant improvements, IT teams should shift their focus from incident volume to incident age.
Most employee devices have critical agent software for tasks like virus protection and encryption. When these agents fail, IT issues are more likely. In order to address this problem, you need to visualize incident age, track its development, and identify which agents are failing.
Let’s start with the management philosophy first and finish with tips and tools to help you move through each stage.
3 Management Stages
1) The first step is establishing a workplace baseline and standardization to create clear boundaries and prevent potential issues. A reactive approach focuses on resolving visible problems, but this doesn't fix the underlying framework issues. Instead, IT teams should ensure that all device components meet expected standards, identify exceptions, and assess the performance of critical agents.
By prioritizing processes and technology to establish an enterprise-wide Standard Operating Environment (SOE), IT teams can monitor compliance and identify risks within exceptions. This proactive framework allows IT teams to quickly address incidents and prevent future problems. Research shows that this approach can eliminate over 30% of recurring incidents.
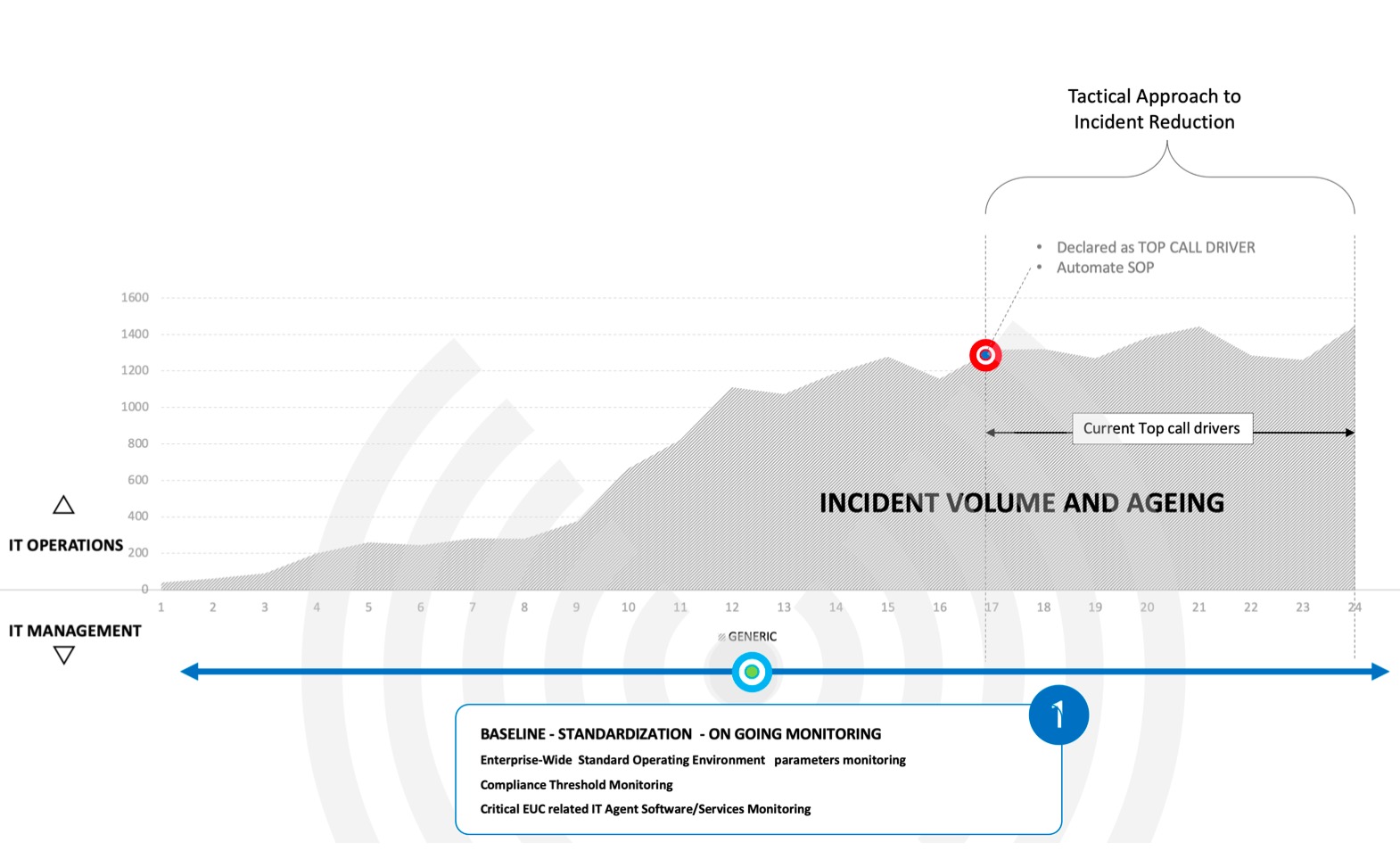
2) Next, with standardization in place, IT teams should optimize their reactive incident reduction strategies. While this doesn’t eliminate existing incidents, it allows teams to resolve them more effectively and reduce their recurrence. This involves identifying high-volume incidents, creating standard operating procedures (SOPs), automating these SOPs, and monitoring for recurrence.
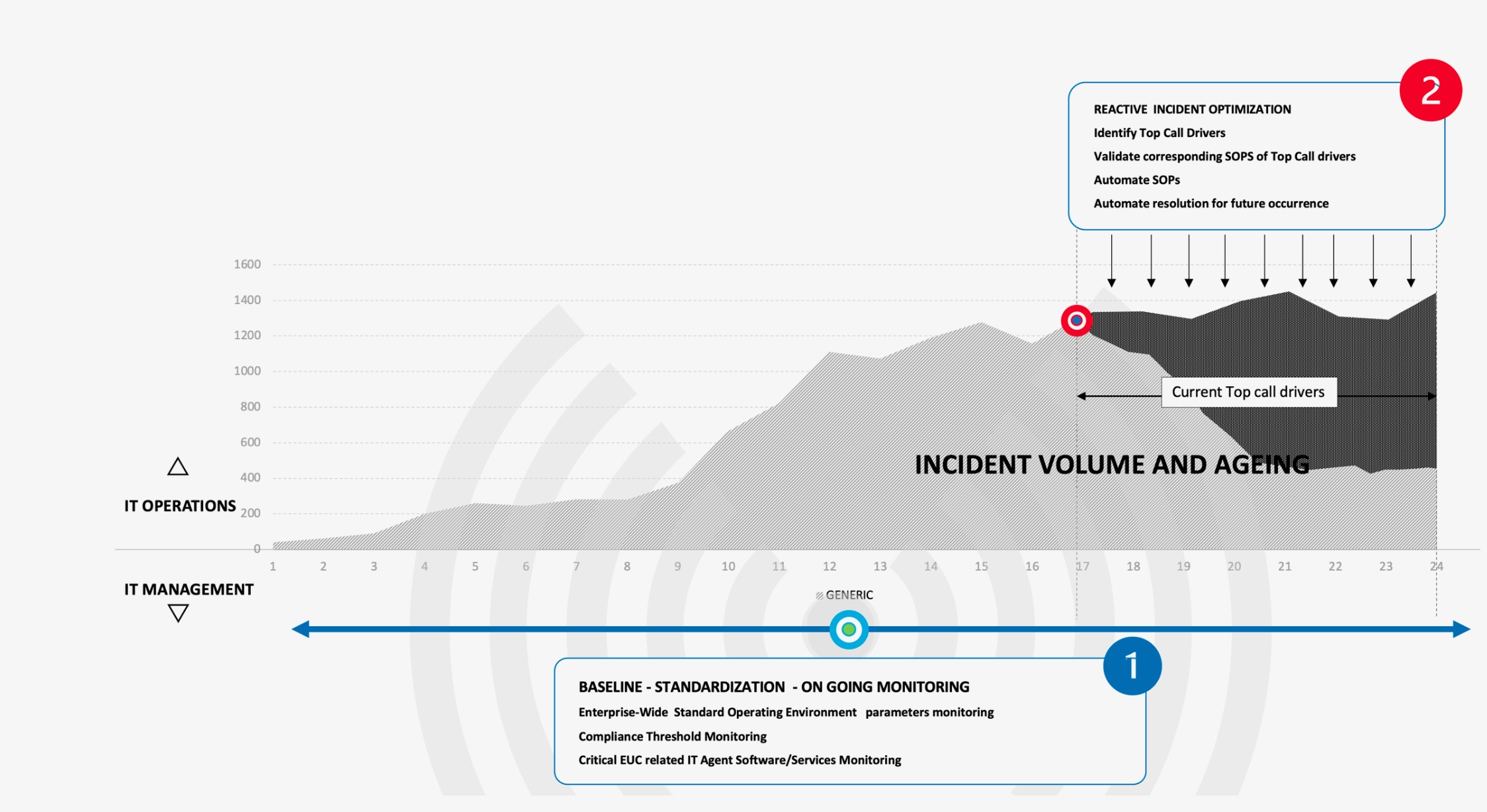
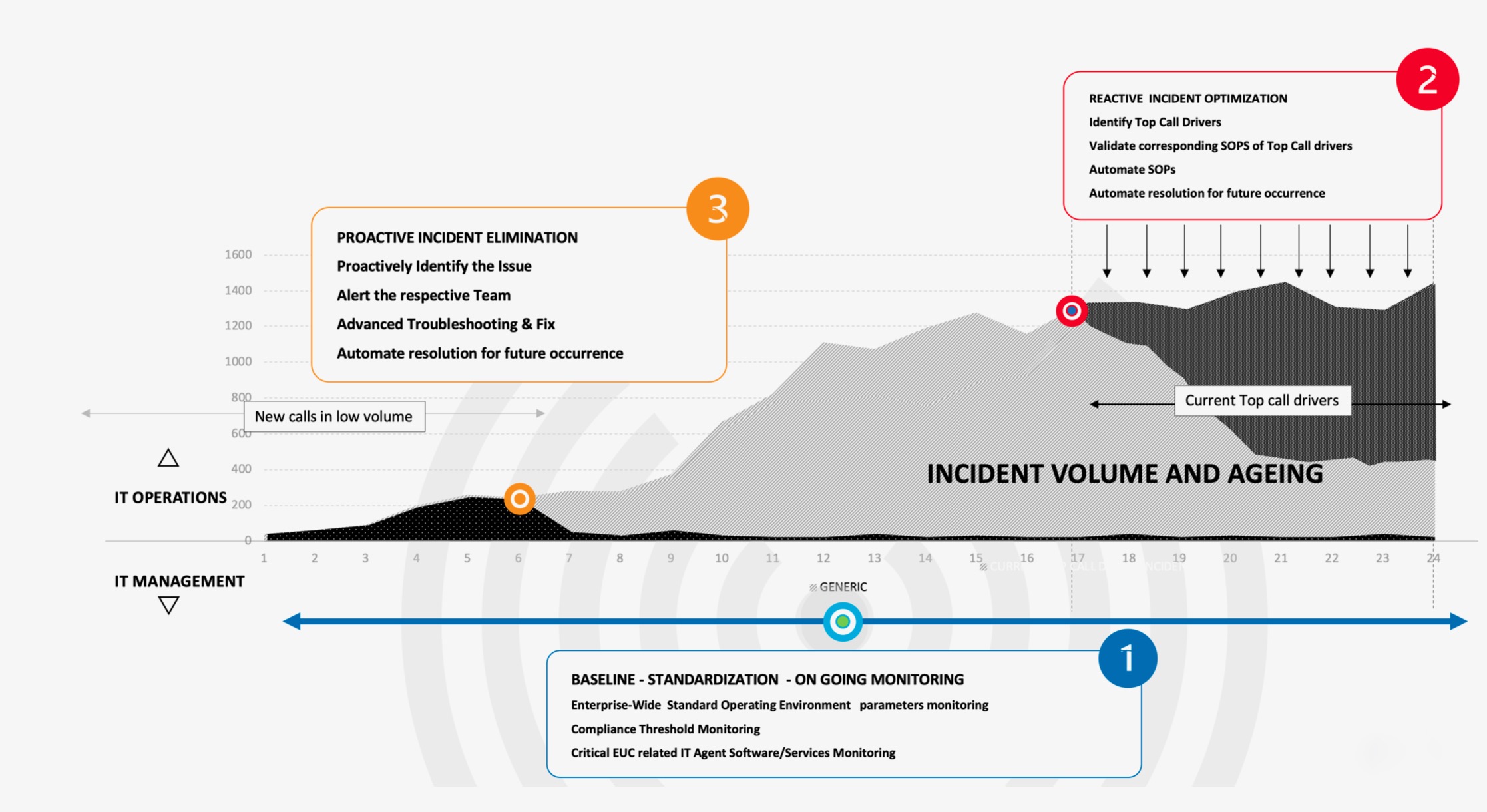
3) IT teams should then evolve from reactive incident reduction to proactive problem elimination. With baselines established and core issues addressed, teams can now focus on preventing new issues from becoming major problems. This requires real-time monitoring of potential issues and providing preventative support before they impact employees. By proactively identifying and resolving low-volume issues early, IT teams can minimize their impact and prevent them from recurring.
A proactive IT framework doesn’t replace the need for reactive problem-solving but complements it by reducing the total number of incidents. Implementing a Digital Employee Experience solution can help build a more efficient IT team that prevents issues rather than just reacting to them, ultimately creating a better workplace experience for employees.
8 Pieces of Advice to Help You Along The Way
1. Leverage AI and Machine Learning:
- Predictive Analytics: Utilize AI and machine learning to predict potential issues before they arise. Predictive analytics can help identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate future problems.
- Automated Incident Detection: Implement AI-driven tools that can automatically detect and respond to incidents in real-time, minimizing downtime and impact on employees.
2. Implement Continuous Monitoring:
- Real-Time Monitoring Tools: Deploy real-time monitoring tools to keep an eye on network performance, system health, and application functionality. Tools like Splunk, New Relic, or Nagios can provide real-time alerts and insights.
- User Experience Monitoring: Use Digital Employee Experience Management tools to continuously assess the end-user experience. This helps in identifying and addressing issues affecting user productivity.
3. Conduct Regular IT Health Assessments:
- Routine Audits: Perform regular IT health assessments and audits to ensure all systems and software are up to date and functioning correctly. This includes patch management, software updates, and hardware checks.
- Compliance Checks: Ensure that all systems comply with industry standards and regulations to prevent security breaches and other compliance-related issues.
4. Enhance Incident Response Plans:
- Comprehensive Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly update a comprehensive incident response plan. This plan should outline clear steps for identifying, managing, and resolving incidents.
- Simulated Drills: Conduct regular simulated drills and tabletop exercises to test the effectiveness of your incident response plan and make necessary adjustments.
5. Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement:
- Feedback Loops:** Establish feedback loops with employees to gather insights on recurring issues and areas for improvement. Regularly review and act on this feedback.
- Post-Incident Reviews: Conduct post-incident reviews to analyze the root causes of incidents and identify preventive measures. Share lessons learned across the team to improve future responses.
6. Invest in Employee Training and Awareness:
- Regular Training Sessions: Provide regular training sessions for employees on IT best practices, security awareness, and new technologies. Well-informed employees are less likely to cause unintentional incidents.
- Awareness Campaigns: Run awareness campaigns to educate employees about common IT issues and how they can help prevent them.
7. Utilize IT Service Management (ITSM) Tools:
- Comprehensive ITSM Platforms: Implement ITSM tools like ServiceNow, BMC Helix, or Jira Service Management to streamline incident management processes, automate workflows, and track incident lifecycle efficiently.
- Self-Service Portals: Create self-service portals where employees can find solutions to common issues, reducing the number of support tickets and empowering users to resolve minor problems independently.
8. Collaborate Across Departments:
- Inter-Departmental Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between IT and other departments to understand their specific needs and potential pain points. This helps in creating tailored solutions that prevent incidents specific to those departments.
- Integrated Communication Channels: Use integrated communication channels like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or dedicated IT communication platforms to ensure quick and effective communication during incidents.